TASK 3
Ravi is good in academic and co-curriculum. He is a very talkative person, and always been chosen in school debate and forum. In addition, he is the best student in his batch and at the same time, he is also a leader for his school football team. Last week, when he was back from football practice, he involved in a road accident with a severe head injured. He was coma in hospital for one week. His mother worries whether the accident will affect his ability to speak and hear. On the other hand, his football coach and teammates worried about his performance in the coming football match. His teacher concerned about his performance in academic.
As an Animal Physiology undergraduate student, what your justification about his condition that occur in his central nervous system.
FILA CHART
TASK 3
QUESTION 1
What is central nervous system?
The part of the nervous system that coordinates the activity of all parts of the bodies. It consists of the Brain and Spinal Cord.
QUESTION 2
What is function of brain?
Brain is the boss of our body. It runs the show and controls just about everything we do.
QUESTION 3
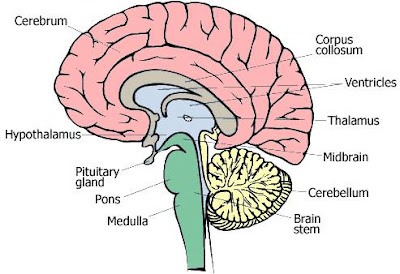
What are the structures of human brain?
• Brain stem - The brain stem consists of the medulla (an enlarged portion of the upper spinal cord), pons and midbrain (lower animals have only a medulla). The brain stem controls the reflexes and automatic functions (heart rate, blood pressure), limb movements and visceral functions (digestion, urination).
• Cerebellum - The cerebellum integrates information from the vestibular system that indicates position and movement and uses this information to coordinate limb movements.
• Hypothalamus and pituitary gland - These control visceral functions, body temperature and behavioral responses such as feeding, drinking, sexual response, aggression and pleasure.
• Cerebrum (also called the cerebral cortex or just the cortex) – the cerebrum consists of the cortex, large fiber tracts (corpus callosum) and some deeper structures (basal ganglia, amygdala, hippocampus). It integrates information from all of the sense organs, initiates motor functions, controls emotions and holds memory and thought processes (emotional expression and thinking are more prevalent in higher mammals).
QUESTION 4
What is function of cerebrum?
The cerebrum or cortex is the largest part of the human brain, associated with higher brain function such as thought and action. The cerebral cortex is divided into four sections, called "lobes": the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe. Here is a visual representation of the cortex:


What does each of these lobes do?
• Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving
• Parietal Lobe- associated with movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli
• Occipital Lobe- associated with visual processing
• Temporal Lobe- associated with perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech
1. The cerebral cortex is highly wrinkled. Essentially this makes the brain more efficient, because it can increase the surface area of the brain and the amount of neurons within it.
2. A deep furrow divides the cerebrum into two halves, known as the left and right hemispheres.
3. The two hemispheres look mostly symmetrical yet it has been shown that each side functions slightly different than the other.
4. Sometimes the right hemisphere is associated with creativity and the left hemispheres are associated with logic abilities.
5. The corpus callosum is a bundle of axons which connects these two hemispheres.
QUESTION 5:
What are the effects of damage of cerebrum?
The listed Functions cannot occur as normal person.
Movement
The cerebrum directs the conscious or volitional motor functions of the body. These functions originate within the primary motor cortex and other frontal lobe motor areas where actions are planned. Upper motor neurons in the primary motor cortex send their axons to the brainstem and spinal cord to synapse on the lower motor neurons, which innervate the muscles. Damage to motor areas of cortex can lead to certain types of motor neuron disease. This kind of damage results in loss of muscular power and precision rather than total paralysis.
Sensory processing
The primary sensory areas of the cerebral cortex receive and process visual, auditory, somatosensory, gustatory, and olfactory information. Together with association cortical areas, these brain regions synthesize sensory information into our perceptions of the world around us.
Olfaction
The olfactory bulb in most vertebrates is the most anterior portion of the cerebrum, and makes up a relatively large proportion of the telencephalon. However, in humans, this part of the brain is much smaller, and lies underneath the frontal lobe. The olfactory sensory system is unique in the sense that neurons in the olfactory bulb send their axons directly to the olfactory cortex, rather than to the thalamus first. Damage to the olfactory bulb results in a loss of the sense of smell.
Language and communication
Speech and language are mainly attributed to parts of the cerebral cortex. Motor portions of language are attributed to Broca's area within the frontal lobe. Speech comprehension is attributed to Wernicke's area, at the temporal-parietal lobe junction.
QUESTION 6:
What part of central nervous system involve in movement?
The cerebrum directs the conscious or volitional motor functions of the body. These functions originate within the primary motor cortex and other frontal lobe motor areas where actions are planned. Upper motor neurons in the primary motor cortex send their axons to the brainstem and spinal cord to synapse on the lower motor neurons, which innervate the muscles.
QUESTION 7
What is function of brain stem?

The brain stem plays a vital role in basic attention, arousal, and consciousness. All information from or to our body passes through the brain stem on the way to or from the brain. The brain stem is located in an area near bony protrusions making it vulnerable to damage during trauma. It is also responsible for basic vital life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure. Furthermore, it also can control sweating, digestion and temperature.
QUESTION 8
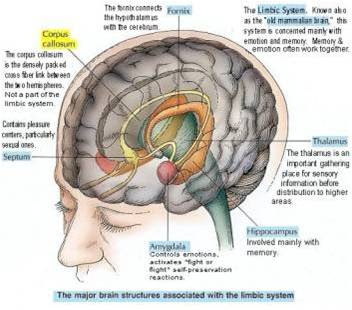
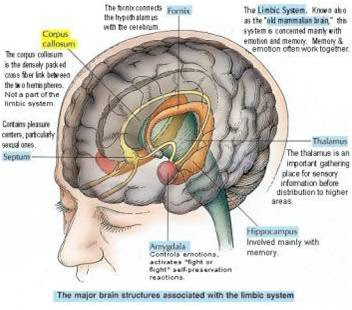
What is function of limbic system?
The limbic system is a complex set of structures that lies on both sides of the thalamus, just under the cerebrum. It includes the hypothalamus, the hippocampus, the amygdala, and several other nearby areas. It is also contains the brain's reward circuit. It links together a number of brain structures that control and regulate our ability to feel pleasure. Feeling pleasure motivates us to repeat behaviors such as eating an actions that are critical to our existence. The limbic system is activated when we perform these activities and also by drugs of abuse. In addition, the limbic system is responsible for our perception of other emotions, both positive and negative, which explains the mood and has a lot to do with the formation of memories.
QUESTION 9
Why Ravi’s nervous system not functions?
Ravi’s nervous system not functions because of the blood clotting. This occurs when bleeding takes place between the brain and the skull. The blood then forms a clot, which puts pressure on brain tissue, which in turn affects the brain's functions. The symptom of this illness are confusion, slow-thinking, personality changes, headaches, mild paralysis, brief episodes of speaking difficulties may occur and seizures. In this case, this illness causes by head injury and bleeding problems. Ravi’s can treat this illness by doing Corticosteroid medication but it may be sufficient for some patients. He also can make a surgical removal of blood clot.
QUESTION 10
How bloods clotting in the brain occur?
A blood clot is formed in the brain, due to bleeding that takes place in the area between the skull and brain. This blood forms a clot, which eventually puts pressure on brain tissue. Functioning of the brain is affected due to pressure that is exerted on the brain. Head injury often is the most common cause of blood clot in the brain. . Blood clots have a tendency to break away from the area, where it was formed and move to different areas. The clot can blocks blood supply when it moves to another part of the body and causes a stroke. There are several symptoms of a blood clot in the brain:
1) Confusion and slow thinking
2) Speaking difficulties
3) Loss of coordination
4) Depression
5) Paralysis
6) Blindness
7) Seizures
8) Headaches
No comments:
Post a Comment